# Table of Contents
# Elasticsearch
Elasticsearch은 Apache Lucene 기반의 Java 오픈 소스 분산 검색 엔진이다.관계형 데이터베이스는 행의 위치인
인덱스(Index)를 사용하여 행을 조회한다. 반면 ElasticSearch은 도큐먼트의 문자, 단어 등을 매핑한역색인(Inverted Index)을 사용하여 데이터를 조회한다. 일반 인덱스는 책 앞 페이지의 목차와 같은 의미이고, 역색인은 책 뒷 편의 단어 별 빠른 페이지와 같다.인덱스를 통한 검색은 인덱스를 순차검색 하기 때문에
O(n)또는O(logn)의 시간 복잡도를 갖는다. 반면 역색인은 마치 해시함수와 같아서O(1)의 시간 복잡도를 갖는다. 이 때문에 ElasticSearch은 빠른 검색에 사용된다.ElasticSearch는 스키마가 없기 때문에 NoSQL처럼 비정형 데이터를 저장할 수 있다. 물론
Mapping을 사용하면 스키마를 설정할 수도 있다.ElasticSearch는 기본적으로 REST API에 HTTP 요청을 보내는 형태로 데이터를 조작한다.
RDBMS Elastic Search SELECT GET UPDATE PUT INSERT POST DELETE DELETE
# ELK 스택
Elasticsearch은 빠른 검색을 위해 단독으로 사용되기도 하지만ELK(Elasticsearch / LogStash / Kibana)+Beats스택으로 사용되기도 한다.- ELK 스택을 사용하면 여러 데이터소스에서 발생한 데이터를 수집, 가공, 분석한 후 시각화할 수 있다.
- ELK 스택은 MSA 환경에서 여러 개별 서비스의 로그를 중앙 집중형 로깅하고 모니터링하는데 사용할 수 있다.
- 빅데이터 분야에도 활용할 수 있다.
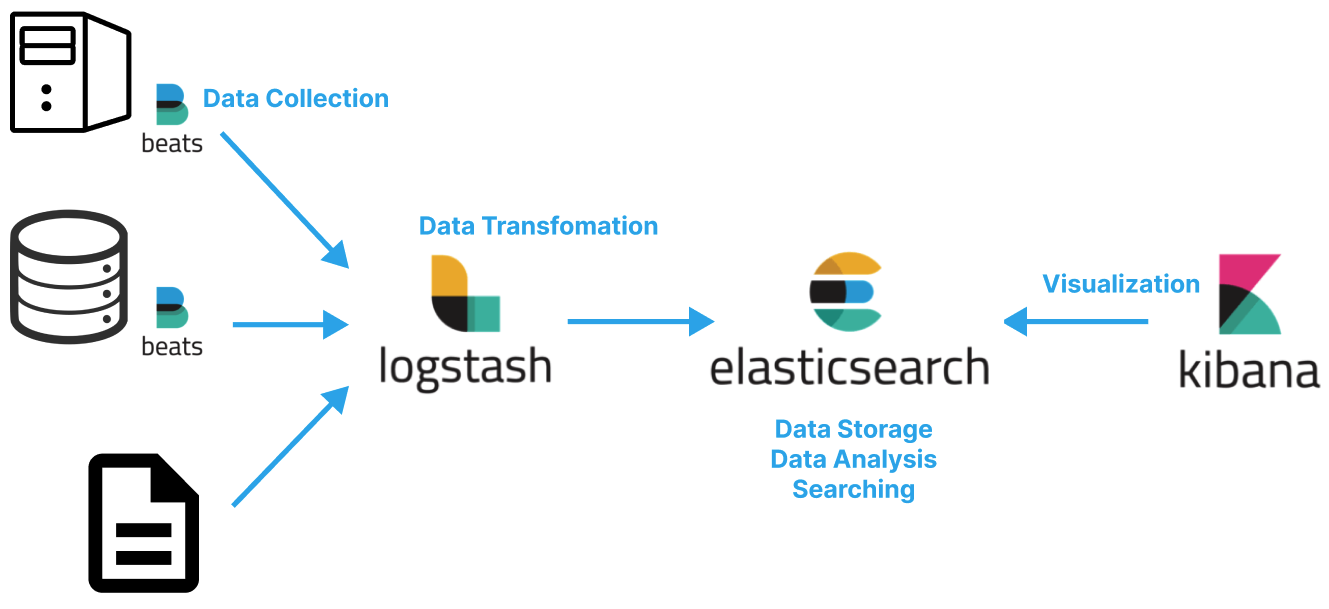
# Beats
- 여러 데이터 소스에 설치되어 데이터를 수집한 후 Logstash로 전송한다.
# Logstash
- 데이터 소스의 데이터를 실시간으로 수집하여 Elastic Search로 전달하는 파이프 라인 엔진이다.
- 여러 데이터 소스로부터 발생하는 데이터를 적절하게 변환한다.
# Elasticsearch
- Logstash를 통해 수신된 데이터를 저장소에 저장하는 역할을 담당한다.
- 역인덱싱을 통한 빠른 검색을 제공한다.
- 어그리게이션 등을 통한 데이터 가공 및 분석 기능을 제공한다.
# Kibana
- ElasticSearch에 저장된 데이터를 시각화한다.
# Elasticsearch 설치
Information
ElasticSearch 7.17.4 버전을 기준으로 합니다.
Mac OS 환경에서는 Homebrew로 쉽게 설치할 수 있다.
$ brew install elastic/tap/elasticsearch-full
$ brew info elastic/tap/elasticsearch-full
elastic/tap/elasticsearch-full: stable 7.17.4
Distributed search & analytics engine
https://www.elastic.co/products/elasticsearch
Conflicts with:
elasticsearch
/usr/local/Cellar/elasticsearch-full/7.17.4 (946 files, 476.2MB) *
Built from source on 2022-06-07 at 03:21:58
From: https://github.com/elastic/homebrew-tap/blob/HEAD/Formula/elasticsearch-full.rb
==> Caveats
Data: /usr/local/var/lib/elasticsearch/elasticsearch_hyukjung/
Logs: /usr/local/var/log/elasticsearch/elasticsearch_hyukjung.log
Plugins: /usr/local/var/elasticsearch/plugins/
Config: /usr/local/etc/elasticsearch/
설치가 완료되었다면 다음과 같이 시작할 수 있다.
$ brew services start elastic/tap/elasticsearch-full
$ brew services list
Name Status User File
elasticsearch-full started yologger ~/Library/LaunchAgents/homebrew.mxcl.elasticsearch-full.plist
참고로 다음과 같이 Elastic Search를 종료할 수 있다.
$ brew services stop elastic/tap/elasticsearch-full
# Index
인덱스(Index)는 관계형 데이터베이스의 데이터베이스에 상응한다.
# 모든 인덱스 조회
모든 인덱스는 다음과 같이 조회할 수 있다.
$ curl -XGET http://localhost:9200/_cat/indices?v
health status index uuid pri rep docs.count docs.deleted store.size pri.store.size
green open .geoip_databases SulDhHIrS0m9Saj_8dDmiw 1 0 40 37 38.2mb 38.2mb
green open .apm-custom-link RnYiMMZaQG2-wIGVOOHO9g 1 0 0 0 226b 226b
green open .apm-agent-configuration dZ38RFD3TxeX1i5Qew_iag 1 0 0 0 226b 226b
green open .kibana_task_manager_7.17.4_001 v9bQStFQQwirWPuyzHcXSA 1 0 17 63369 7.1mb 7.1mb
green open .kibana_7.17.4_001 NJda68wDRoOK213SMSOuXQ 1 0 316 24 2.4mb 2.4mb
green open .tasks TChPhQP_RymhB-xr0TdxuQ 1 0 4 0 27.4kb 27.4kb
# 인덱스 생성
다음과 같이 인덱스를 생성할 수 있다.
$ curl -XPUT http://localhost:9200/<INDEX_NAME>
$ curl -XPUT http://localhost:9200/person
{"acknowledged":true,"shards_acknowledged":true,"index":"person"}
# 인덱스 정보 조회
다음과 같이 인덱스에 대한 정보를 조회할 수 있다.
$ curl -XGET http://localhost:9200/<INDEX_NAME>
$ curl -XGET http://localhost:9200/person
{"person":{"aliases":{},"mappings":{},"settings":{"index":{"routing":{"allocation":{"include":{"_tier_preference":"data_content"}}},"number_of_shards":"1","provided_name":"person","creation_date":"1654690323178","number_of_replicas":"1","uuid":"b-Lm10C-RBOqo8JlYSqw8A","version":{"created":"7170499"}}}}}
인덱스가 없다면 다음과 같은 오류가 발생한다.
{"error":{"root_cause":[{"type":"index_not_found_exception","reason":"no such index [person]","resource.type":"index_or_alias","resource.id":"person","index_uuid":"_na_","index":"person"}],"type":"index_not_found_exception","reason":"no such index [person]","resource.type":"index_or_alias","resource.id":"person","index_uuid":"_na_","index":"person"},"status":404}
pretty 옵션으로 결과값을 예쁘게 출력할 수 있다.
$ curl -XGET http://localhost:9200/person?pretty
{
"person" : {
"aliases" : { },
"mappings" : { },
"settings" : {
"index" : {
"routing" : {
"allocation" : {
"include" : {
"_tier_preference" : "data_content"
}
}
},
"number_of_shards" : "1",
"provided_name" : "person",
"creation_date" : "1654690323178",
"number_of_replicas" : "1",
"uuid" : "b-Lm10C-RBOqo8JlYSqw8A",
"version" : {
"created" : "7170499"
}
}
}
}
}
# 인덱스 삭제
다음과 같이 인덱스를 삭제할 수 있다.
$ curl -XDELETE http://localhost:9200/person
{"acknowledged":true}
# Document
# 도큐먼트 생성
도큐먼트를 생성할 때는 HTTP PUT 메소드를 사용한다.
$ curl -XPUT http://localhost:9200/<INDEX>/_doc/<DOCUMENT_ID> \
- H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
- d '{"key": "value"}'
$ curl -XPUT http://localhost:9200/player/_doc/1?pretty \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{"name": "messi", "nation": "argentina"}'
도큐먼트 생성에 성공하면 "result" : "created"가 표시된다.
{
"_index" : "player",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_version" : 1,
"result" : "created",
"_shards" : {
"total" : 2,
"successful" : 1,
"failed" : 0
},
"_seq_no" : 0,
"_primary_term" : 1
}
동일한 URL에 다른 도큐먼트를 입력하면 기존 도큐먼트를 덮어쓰게 되며 "result" : "updated"가 표시된다. 또한 "_version"의 값이 1 증가한다.
$ curl -XPUT http://localhost:9200/player/_doc/1?pretty \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{"name": "ronaldo", "nation": "portugal"}'
{
"_index" : "player",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_version" : 2,
"result" : "updated",
"_shards" : {
"total" : 2,
"successful" : 1,
"failed" : 0
},
"_seq_no" : 1,
"_primary_term" : 1
}
도큐먼트는 JSON 파일을 사용하여 생성할 수도 있다.
// player.json
{
"name": "benzema",
"nation": "france"
}
$ curl -XPOST http://localhost:9200/player/_doc/3 \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d @player.json
ID 없이 도큐먼트를 생성하면 ID가 자동으로 생성된다.
$ curl -XPOST http://localhost:9200/player/_doc?pretty \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{"name": "neymar", "nation": "brazil"}'
{
"_index" : "player",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "QCFIQ4EBhCK0-IfWXiwB",
"_version" : 1,
"result" : "created",
"_shards" : {
"total" : 2,
"successful" : 1,
"failed" : 0
},
"_seq_no" : 2,
"_primary_term" : 1
}
실수로 기존 도큐먼트가 덮어씌워지는 것을 방지하기 위해 _doc 대신 _create를 사용하여 도큐먼트를 생성할 수 있다.
$ curl -XPOST http://localhost:9200/player/_create/1?pretty \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{"name": "kane", "nation": "england"}'
도큐먼트가 이미 존재하는 경우 다음 에러가 발생한다.
{
"error" : {
"root_cause" : [
{
"type" : "version_conflict_engine_exception",
"reason" : "[1]: version conflict, document already exists (current version [2])",
"index_uuid" : "wIiKCmHQSYijirqahH_tpw",
"shard" : "0",
"index" : "player"
}
],
"type" : "version_conflict_engine_exception",
"reason" : "[1]: version conflict, document already exists (current version [2])",
"index_uuid" : "wIiKCmHQSYijirqahH_tpw",
"shard" : "0",
"index" : "player"
},
"status" : 409
}
# 도큐먼트 조회
도큐먼트를 조회할 때는 HTTP GET 메서드를 사용한다.
$ curl -XGET http://localhost:9200/player/_doc/1?pretty
{
"_index" : "player",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_version" : 2,
"_seq_no" : 1,
"_primary_term" : 1,
"found" : true,
"_source" : {
"name" : "ronaldo",
"nation" : "portugal"
}
}
# 도큐먼트 업데이트
다음과 같은 도큐먼트가 있다고 하자.
$ curl -XGET http://localhost:9200/player/_doc/1?pretty
{
"_index" : "player",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_version" : 2,
"_seq_no" : 1,
"_primary_term" : 1,
"found" : true,
"_source" : {
"name" : "ronaldo",
"nation" : "portugal"
}
}
URL 뒤에 _update을 붙이면 특정 필드만 업데이트할 수 있다. Request Body에는 doc 키를 통해 변경할 내용을 전달한다.
$ curl -XPOST http://localhost:9200/player/_update/1?pretty \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{"doc": {"name": "pepe"}}'
$ curl -XGET http://localhost:9200/player/_doc/1\?pretty
{
"_index" : "player",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_version" : 3,
"_seq_no" : 3,
"_primary_term" : 1,
"found" : true,
"_source" : {
"name" : "pepe",
"nation" : "portugal"
}
}
특정 필드를 추가할 수도 있다.
$ curl -XPOST http://localhost:9200/player/_update/1?pretty \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{"doc": {"team": "real madrid"}}'
$ curl -XGET http://localhost:9200/player/_doc/1?pretty
{
"_index" : "player",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_version" : 4,
"_seq_no" : 4,
"_primary_term" : 1,
"found" : true,
"_source" : {
"name" : "pepe",
"nation" : "portugal",
"team" : "real madrid"
}
}
doc 대신 script 키를 통해 계산식을 사용할 수도 있다.
$ curl -XPOST http://localhost:9200/person/player/2/_update \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{"script": "ctx._source.age += 5"}'
$ curl -XGET http://localhost:9200/person/player/2\?pretty
{
"_index" : "person",
"_type" : "player",
"_id" : "2",
"_version" : 6,
"_seq_no" : 6,
"_primary_term" : 1,
"found" : true,
"_source" : {
"name" : "Smith",
"nation" : "UK",
"team" : "real madrid",
"age" : 40
}
}
# 도큐먼트 삭제
HTTP DELETE 메소드로 도큐먼트를 삭제할 수 있다.
$ curl -XDELETE http://localhost:9200/player/_doc/1?pretty
{
"_index":"player",
"_type":"_doc",
"_id":"1",
"_version":5,
"result":"deleted",
"_shards":{
"total":2,
"successful":1,
"failed":0
},
"_seq_no":5,
"_primary_term":1
}
# 벌크 작업
ElasticSearch는 벌크 작업도 지원한다.
JSON 파일로 벌크 INSERT 작업을 수행해보자.
// players.json
{ "index" : { "_index" : "player", "_id" : "1" } }
{"name": "ronaldo", "nation": "portugal", "age": 37, "score": 15, "assist": 15}
{ "index" : { "_index" : "player", "_id" : "2" } }
{"name": "son", "nation": "south korea", "age": 31, "score": 20, "assist": 13}
{ "index" : { "_index" : "player", "_id" : "3" } }
{"name": "salah", "nation": "egypt", "age": 31, "score": 19, "assist": 11}
{ "index" : { "_index" : "player", "_id" : "4" } }
{"name": "benzema", "nation": "france", "age": 36, "score": 27, "assist": 11}
{ "index" : { "_index" : "player", "_id" : "5" } }
{"name": "ebappe", "nation": "france", "age": 25, "score": 25, "assist": 7}
{ "index" : { "_index" : "player", "_id" : "6" } }
{"name": "pogba", "nation": "france", "age": 31, "score": 8, "assist": 20}
{ "index" : { "_index" : "player", "_id" : "7" } }
{"name": "kane", "nation": "england", "age": 30, "score": 12, "assist": 18}
{ "index" : { "_index" : "player", "_id" : "8" } }
{"name": "fernandes", "nation": "portugal", "age": 28, "score": 10, "assist": 16}
--data-binary옵션을 사용하면 된다.
$ curl -XPOST http://localhost:9200/player/_bulk \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-binary @players.json
# 검색
URL 뒤에 _search를 붙여 도큐먼트를 검색할 수 있다.
$ curl -XGET http://localhost:9200/player/_search\?pretty
{
"took" : 0,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 8,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 1.0,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "player",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"name" : "ronaldo",
"nation" : "portugal",
"age" : 37,
"score" : 15,
"assist" : 15
}
},
{
"_index" : "player",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "2",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"name" : "son",
"nation" : "south korea",
"age" : 31,
"score" : 20,
"assist" : 13
}
},
{
"_index" : "player",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "3",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"name" : "salah",
"nation" : "egypt",
"age" : 31,
"score" : 19,
"assist" : 11
}
},
{
"_index" : "player",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "4",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"name" : "benzema",
"nation" : "france",
"age" : 36,
"score" : 27,
"assist" : 11
}
},
{
"_index" : "player",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "5",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"name" : "ebappe",
"nation" : "france",
"age" : 25,
"score" : 25,
"assist" : 7
}
},
{
"_index" : "player",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "6",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"name" : "pogba",
"nation" : "france",
"age" : 31,
"score" : 8,
"assist" : 20
}
},
{
"_index" : "player",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "7",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"name" : "kane",
"nation" : "england",
"age" : 30,
"score" : 12,
"assist" : 18
}
},
{
"_index" : "player",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "8",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"name" : "fernandes",
"nation" : "portugal",
"age" : 28,
"score" : 10,
"assist" : 16
}
}
]
}
}
조건을 쿼리 파라미터 형태로 전달할 수 있다. _search 뒤에 q 파라미터를 추가하면 된다.
$ curl -XGET http://localhost:9200/player/_search?q=age:36&pretty
{
"took" : 0,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 1,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 1.0,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "player",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "4",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"name" : "benzema",
"nation" : "france",
"age" : 36,
"score" : 27,
"assist" : 11
}
}
]
}
}
조건을 HTTP request body 형태로 전달할 수도 있다.
$ curl -XGET http://localhost:9200/player/_search\?pretty \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{ "query": { "match": {"name": "kane"} }}'
{
"took" : 0,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 1,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 1.7917595,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "player",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "7",
"_score" : 1.7917595,
"_source" : {
"name" : "kane",
"nation" : "england",
"age" : 30,
"score" : 12,
"assist" : 18
}
}
]
}
}
다양한 검색 옵션을 좀 더 알아보자.
# 예제 코드
예제를 위한 데이터는 다음과 같다.
{"index":{"_id":1, "_index" : "post"}}
{"content":"hello world"}
{"index":{"_id":2, "_index" : "post"}}
{"content":"hello world nice to meet you"}
{"index":{"_id":3, "_index" : "post"}}
{"content":"hello world see you again"}
{"index":{"_id":4, "_index" : "post"}}
{"content":"see you again good bye"}
{"index":{"_id":5, "_index" : "post"}}
{"content":"good bye have a nice day"}
{"index":{"_id":6, "_index" : "post"}}
{"content":"hello world nice to meet you good bye have a nice day"}
$ curl -XPOST http://localhost:9200/post/_bulk \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-binary @posts.json
# Term 쿼리
Term 쿼리는 검색어에 대한 분석을 하지않고 온전히 그 검색어와 일치하는 문서를 검색한다. 아래 예제에서는 정확히 again을 포함한 도큐먼트만 결과물로 출력한다.
$ curl -XGET http://localhost:9200/post/_search?pretty \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '
{
"query": {
"term": {
"content": "again"
}
}
}
'
{
"took" : 0,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 2,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 1.1049575,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "post",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "3",
"_score" : 1.1049575,
"_source" : {
"content" : "hello world see you again"
}
},
{
"_index" : "post",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "4",
"_score" : 1.1049575,
"_source" : {
"content" : "see you again good bye"
}
}
]
}
}
# Match 쿼리
Term 쿼리가 완전히 정확한 검색이라면 Match 쿼리는 다소 모호한 검색이다. 예를 들어 여러 도큐먼트에 do, done, doing의 단어가 포함되어있고 용어(Term)에 do가 등록되어있다면 do 뿐만 아니라 done, doing을 포함하는 도큐먼트도 검색해준다.
$ curl -XGET http://localhost:9200/post/_search?pretty \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '
{
"query": {
"match": {
"content": "hello"
}
}
}
'
{
"took" : 0,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 4,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 0.60752,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "post",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 0.60752,
"_source" : {
"content" : "hello world"
}
},
{
"_index" : "post",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "3",
"_score" : 0.47416198,
"_source" : {
"content" : "hello world see you again"
}
},
{
"_index" : "post",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "2",
"_score" : 0.44183272,
"_source" : {
"content" : "hello world nice to meet you"
}
},
{
"_index" : "post",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "6",
"_score" : 0.3135587,
"_source" : {
"content" : "hello world nice to meet you good bye have a nice day"
}
}
]
}
}
match 검색에 여러 개의 검색어를 넣으면 OR 조건으로 검색을 한다.
$ curl -XGET http://localhost:9200/post/_search?pretty \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '
{
"query": {
"match": {
"content": "hello nice"
}
}
}
'
{
"query": {
"match": {
"content": "hello nice"
}
}
}
'
{
"took" : 40,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 5,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 1.1349798,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "post",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "2",
"_score" : 1.1349798,
"_source" : {
"content" : "hello world nice to meet you"
}
},
{
"_index" : "post",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "6",
"_score" : 1.057424,
"_source" : {
"content" : "hello world nice to meet you good bye have a nice day"
}
},
{
"_index" : "post",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "5",
"_score" : 0.6931471,
"_source" : {
"content" : "good bye have a nice day"
}
},
{
"_index" : "post",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 0.60752,
"_source" : {
"content" : "hello world"
}
},
{
"_index" : "post",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "3",
"_score" : 0.47416198,
"_source" : {
"content" : "hello world see you again"
}
}
]
}
}
다음과 같이 AND 조건으로 검색할 수도 있다.
$ curl -XGET http://localhost:9200/post/_search?pretty \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '
{
"query": {
"match": {
"content": "hello nice",
"operator": "and"
}
}
}
'
# Match Phrase 쿼리
$ curl -XGET http://localhost:9200/post/_search?pretty \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '
{
"query": {
"match_phrase": {
"content": "again good"
}
}
}
'
{
"took" : 56,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 1,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 1.8488227,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "post",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "4",
"_score" : 1.8488227,
"_source" : {
"content" : "see you again good bye"
}
}
]
}
}
# Mapping
ElasticSearch는 자유로운 형태로 도큐먼트를 추가할 수 있다. 그러나 매핑(Mapping)을 사용하면 관계형 데이터베이스의 스키마처럼 형식을 강제할 수 있다.
ElasticSearch는 별도의 매핑을 정의하지 않아도 도큐먼트를 새로 추가할 때 매핑이 자동으로 생성된다. 다음과 같이 도큐먼트를 추가하면
$ curl -XPOST http://localhost:9200/player/_doc/1 \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{"name": "ronaldo", "nation": "portugal", "age": 37, "score": 15, "assist": 15}'
다음과 같이 매핑이 자동으로 생성된다.
$ curl -XGET http://localhost:9200/player/_mapping?pretty
{
"player" : {
"mappings" : {
"properties" : {
"age" : {
"type" : "long"
},
"assist" : {
"type" : "long"
},
"name" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"nation" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"score" : {
"type" : "long"
}
}
}
}
}
# 매핑 조회
URL 뒤에 _mapping을 붙여 인덱스의 매핑을 확인할 수 있다. 매핑이 없다면 다음과 같이 출력된다.
$ curl -XPUT http://localhost:9200/post
$ curl -XGET http://localhost:9200/post/_mapping\?pretty
{
"post" : {
"mappings" : { }
}
}
# 매핑 생성
인덱스를 생성할 때 매핑을 함께 정의할 수 있다.
$ curl -XPUT http://localhost:9200/person \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"name": { "type": "text" },
"age": { "type": "integer" }
}
}
}
'
이미 매핑이 존재할 때 필드를 추가할 수도 있다.
$ curl -XPUT http://localhost:9200/person/_mapping \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '
{
"properties": {
"nation": { "type": "text" }
}
}
'
매핑을 확인해보자.
$ curl -XGET http://localhost:9200/person/_mapping\?pretty
{
"person" : {
"mappings" : {
"properties" : {
"age" : {
"type" : "integer"
},
"name" : {
"type" : "text"
},
"nation" : {
"type" : "text"
}
}
}
}
}
이제 매핑에 맞는 형식으로 도큐먼트를 추가해야한다.
$ curl -XPUT http://localhost:9200/player/_doc/1?pretty \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{"name": "paul", "nation": "usa", "age": "35"}'
매핑에 맞지 않는 형식으로 도큐먼트를 추가하면 에러가 발생한다.
curl -XPUT http://localhost:9200/player/_doc/4?pretty \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{"name": "paul", "nation": "usa", "age": "hello world"}'
{
"error" : {
"root_cause" : [
{
"type" : "mapper_parsing_exception",
"reason" : "failed to parse field [age] of type [long] in document with id '4'. Preview of field's value: 'hello world'"
}
],
"type" : "mapper_parsing_exception",
"reason" : "failed to parse field [age] of type [long] in document with id '4'. Preview of field's value: 'hello world'",
"caused_by" : {
"type" : "illegal_argument_exception",
"reason" : "For input string: \"hello world\""
}
},
"status" : 400
}
# 집계
집계(Aggregation)은 모든 데이터의 분석 및 요약을 제공하는 기능이다. 관계형 데이터베이스의 Grouping, Project에 상응한다.
어그리게이션 예제를 위한 테스트 데이터는 다음과 같다.
{ "index" : { "_index" : "person", "_type" : "player", "_id" : "1" } }
{"name": "ronaldo", "nation": "portugal", "age": 37, "score": 15, "assist": 15}
{ "index" : { "_index" : "person", "_type" : "player", "_id" : "2" } }
{"name": "son", "nation": "south korea", "age": 31, "score": 20, "assist": 13}
{ "index" : { "_index" : "person", "_type" : "player", "_id" : "3" } }
{"name": "salah", "nation": "egypt", "age": 31, "score": 19, "assist": 11}
{ "index" : { "_index" : "person", "_type" : "player", "_id" : "4" } }
{"name": "benzema", "nation": "france", "age": 36, "score": 27, "assist": 11}
{ "index" : { "_index" : "person", "_type" : "player", "_id" : "5" } }
{"name": "ebappe", "nation": "france", "age": 25, "score": 25, "assist": 7}
{ "index" : { "_index" : "person", "_type" : "player", "_id" : "6" } }
{"name": "pogba", "nation": "france", "age": 31, "score": 8, "assist": 20}
{ "index" : { "_index" : "person", "_type" : "player", "_id" : "7" } }
{"name": "kane", "nation": "england", "age": 30, "score": 12, "assist": 18}
{ "index" : { "_index" : "person", "_type" : "player", "_id" : "8" } }
{"name": "fernandes", "nation": "portugal", "age": 28, "score": 10, "assist": 16}
$ curl -XPOST http://localhost:9200/_bulk? \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-binary @players.json
# 메트릭 어그리게이션
산술이나 통계에 대한 어그리게이션을 메트릭 어그리게이션이라고 한다.
# 평균 계산하기
// avg_score.json
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"avg_score": {
"avg": { "field": "score" }
}
}
}
$ curl -XGET http://localhost:9200/_search\?pretty \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-binary @avg_score.json
{
"took" : 409,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 8,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : null,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"aggregations" : {
"avg_score" : {
"value" : 17.0
}
}
}
# 최대값 계산하기
// max_score.json
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"max_score": {
"max": { "field": "score" }
}
}
}
# 최소값 계산하기
// min_score.json
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"min_score": {
"min": { "field": "score" }
}
}
}
# 합계 계산하기
// sum_score.json
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"sum_score": {
"sum": { "field": "score" }
}
}
}
# 모든 통계 정보
// stats_score.json
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"stats_score": {
"stats": { "field": "score" }
}
}
}
$ curl -XGET http://localhost:9200/_search\?pretty \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-binary @stats_score.json
{
"took" : 5,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 8,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : null,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"aggregations" : {
"stats_score" : {
"count" : 8,
"min" : 8.0,
"max" : 27.0,
"avg" : 17.0,
"sum" : 136.0
}
}
}
# 버킷 어그리게이션
버킷 어그리게이션는 관계형 데이터베이스의 Group by와 유사하다. 버킷 어그리게이션을 사용하려면 매핑이 추가되어있어야 한다.
// player_mapping.json
{
"player": {
"properties": {
"name": {"type": "text", "fielddata": true},
"nation": {"type": "text", "fielddata": true},
"age": {"type": "long"},
"score": {"type": "long"},
"assist": {"type": "long"}
}
}
}
$ curl -XPUT http://localhost:9200/person/player/_mapping?include_type_name=true&pretty \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d @player_mapping.json
# Terms aggregation
// terms_aggs.json
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"player": {
"terms": { "field": "nation"}
}
}
}
$ curl -XGET http://localhost:9200/_search\?pretty \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-binary @teams_aggs.json
{
"took" : 89,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 8,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : null,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"aggregations" : {
"player" : {
"doc_count_error_upper_bound" : 0,
"sum_other_doc_count" : 0,
"buckets" : [
{
"key" : "france",
"doc_count" : 3
},
{
"key" : "portugal",
"doc_count" : 2
},
{
"key" : "egypt",
"doc_count" : 1
},
{
"key" : "england",
"doc_count" : 1
},
{
"key" : "korea",
"doc_count" : 1
},
{
"key" : "south",
"doc_count" : 1
}
]
}
}
}
← Redis 정리 kibana 시작하기 →
